Extensible Markup Language (XML)
Extensible Markup Language (XML) lets you define and store data in a shareable manner. XML supports information exchange between computer systems such as websites, databases, and third-party applications.
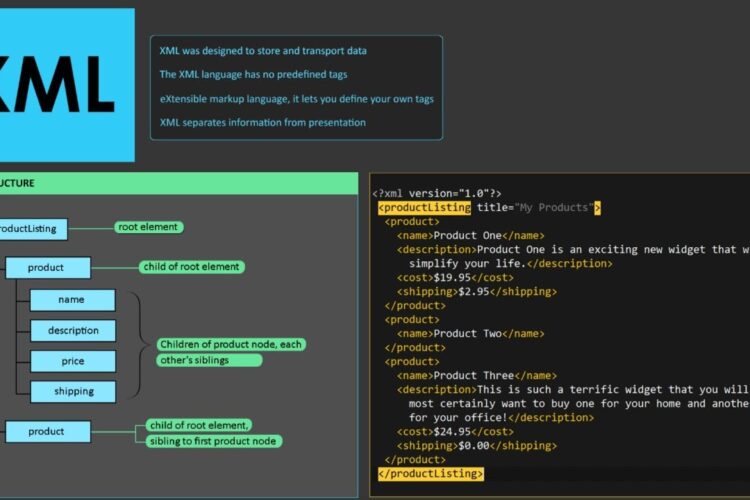
What is XML?
- XML stands for eXtensible Markup Language
- XML is a markup language much like HTML
- XML was designed to store and transport data
- XML was designed to be self-descriptive
- XML is a W3C Recommendation
XML Does Not DO Anything
Maybe it is a little hard to understand, but XML does not DO anything.
This note is a note to Tove from Jani, stored as XML:

The XML above is quite self-descriptive:
- It has sender information
- It has receiver information
- It has a heading
- It has a message body
But still, the XML above does not DO anything. XML is just information wrapped in tags.
The Difference Between XML and HTML
XML and HTML were designed with different goals:
- XML was designed to carry data – with focus on what data is
- HTML was designed to display data – with focus on how data looks
- XML tags are not predefined like HTML tags are